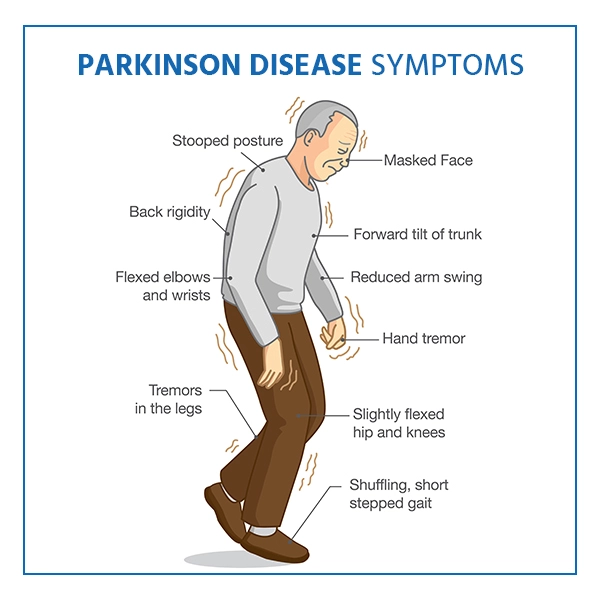
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. It is characterized by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, particularly in a region called the substantia nigra. This loss of dopamine leads to a variety of motor and non-motor symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can be broadly categorized into motor and non-motor symptoms.
Motor Symptoms:
Tremor: Often the first noticeable symptom, tremors typically start in the hand or fingers when at rest.
Bradykinesia: This refers to the slowness of movement, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming.
Rigidity: Muscle stiffness can occur in any part of the body, leading to discomfort and a reduced range of motion.
Postural Instability: Balance problems and a tendency to fall are common in the later stages of the disease.
Non-Motor Symptoms:
Cognitive Impairment: Problems with thinking and memory can develop as the disease progresses.
Mood Disorders: Depression and anxiety are common among individuals with PD.
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia, restless legs syndrome, and REM sleep behavior disorder are frequently reported.
Autonomic Dysfunction: This can include issues with blood pressure regulation, bowel and bladder control, and sexual function.
Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors:
Mutations in certain genes, such as LRRK2, PARK7, PINK1, and SNCA, have been linked to an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. These genetic mutations are more commonly associated with early-onset forms of the disease.
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to certain toxins, such as pesticides and herbicides, has been linked to a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Head injuries and other environmental stressors may also contribute to the disease’s onset.
Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease can be challenging as there are no specific tests for it. Diagnosis is primarily based on medical history, symptoms, and neurological examination. Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may be used to rule out other conditions.
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, various treatments are available to manage its symptoms.
Medications:
Levodopa/Carbidopa: This combination is the most effective treatment for motor symptoms, as Levodopa is converted to dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine Agonists: Medications such as Pramipexole and Ropinirole mimic the effects of dopamine in the brain.
MAO-B Inhibitors: Drugs like Selegiline and Rasagiline inhibit the breakdown of dopamine.
COMT Inhibitors: Entacapone and Tolcapone prolong the effect of Levodopa by inhibiting its breakdown.
Surgical Treatments:
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrodes are implanted in specific brain regions to deliver electrical impulses that help regulate abnormal brain activity.
Supportive Therapies:
Physical Therapy: Helps improve movement, flexibility, and balance.
Occupational Therapy: Assists in adapting daily activities to maintain independence.
Speech Therapy: Addresses speech and swallowing difficulties.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Living with Parkinson’s Disease
Living with Parkinson’s disease can be challenging, but many people continue to lead fulfilling lives with proper management and support. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that meets individual needs.
Support Systems:
Engaging with support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Family and friends play a crucial role in providing care and encouragement.
In conclusion,Parkinson Disease is a complex and multifaceted disorder that requires a comprehensive approach to management. While there is currently no cure, advances in research continue to offer hope for better treatments and improved quality of life for those affected by the disease.
prevent Parkinson’s disease
To prevent Parkinson disease, several lifestyle choices and habits can be beneficial:
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and balance exercises.
Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats.
Brain Stimulation: Keep your brain active by engaging in mentally stimulating activities such as puzzles, reading, or learning new skills.
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good quality sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night.
Avoid Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins such as pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals whenever possible.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Consume alcohol and caffeine in moderation, as excessive intake may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Regular Health Check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly for check-ups and screenings to monitor your overall health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of balanced diet and regular exercise.
Stay Socially Connected: Maintain strong social connections and engage in activities with friends and family to support emotional well-being.
While these lifestyle factors can reduce the risk of Parkinson’s Disease, it’s essential to remember that not all cases can be prevented, as genetics and other factors also play a role.
Important Tips for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Managing Parkinson’s Disease effectively involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive therapies. Here are some essential tips for patients:
1. Regular Exercise
Benefits: Exercise helps improve mobility, flexibility, balance, and overall physical health. It can also alleviate depression and anxiety.
Recommendations: Engage in activities like walking, swimming, strength training, and balance exercises such as yoga and tai chi .
2. Healthy Diet
Benefits: A nutritious diet supports overall health and can help manage symptoms like constipation.
Recommendations: Eat balanced meals that include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins. Avoid processed foods and those high in saturated fats. Staying hydrated is also crucial .
3. Adequate Sleep
Benefits: Quality sleep can enhance energy, focus, and mood, reducing symptoms of depression.
Recommendations: Maintain a regular sleep schedule, create a comfortable sleep environment, and avoid caffeine before bedtime .
4. Medication Management
Benefits: Medications can significantly reduce motor symptoms such as tremors and rigidity.
Recommendations: Follow the prescribed dosage, and discuss any side effects or necessary adjustments with your doctor. Common medications include Levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors .
5. Physical and Occupational Therapy
Benefits: Physical therapy improves movement and strength, while occupational therapy helps with daily activities.
Recommendations: Work with physical and occupational therapists to develop personalized exercise programs and strategies for managing daily tasks .
6. Psychological and Social Support
Benefits: Psychological support can help manage stress, depression, and anxiety, while social support provides a sense of community and belonging.
Recommendations: Join support groups, talk to a counselor or therapist, and stay connected with family and friends .
7. Fall Prevention
Benefits: Preventing falls protects against injuries and enhances personal safety.
Recommendations: Use walking aids if necessary, remove tripping hazards at home, install grab bars where needed, and ensure good lighting throughout the house .
8. Stay Informed About Research
Benefits: Keeping up with new research can provide information about innovative treatments and management strategies.
Recommendations: Follow reputable health news sources, consider participating in clinical trials, and consult with your healthcare provider about new developments .
By incorporating these tips and working closely with healthcare providers, patients with Parkinson’s Disease can improve their quality of life and better manage the challenges of the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions about Parkinson’s Disease
1. What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: Parkinson disease, (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. It is caused by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, particularly in the substantia nigra. This results in symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement).
2. What are the early symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
Tremor in the hand or fingers at rest
Slowed movement (bradykinesia)
Muscle stiffness (rigidity)
Changes in handwriting (micrographia)
Loss of facial expressions (masked face)
3. What causes Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown. It is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic mutations in certain genes, such as LRRK2 and SNCA, and exposure to environmental toxins like pesticides may increase the risk of developing the disease.
4. How is Parkinson’s Disease diagnosed?
Answer: Parkinson disease,is primarily diagnosed based on medical history, symptoms, and a neurological examination. There are no specific tests for PD, but imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may be used to rule out other conditions.
5. What are the treatment options for Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, treatments are available to manage symptoms:
Medications: Levodopa/Carbidopa, dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and COMT inhibitors.
Surgical Treatments: Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for advanced cases.
Supportive Therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise and a healthy diet.
6. Can Parkinson’s Disease be cured?
Answer: Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson disease,However, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
7. How does Parkinson’s Disease affect daily life?
Answer: Parkinson’s disease can impact daily activities due to symptoms like tremors, stiffness, and slowed movement. Patients may need assistance with tasks such as dressing, eating, and walking. Support from healthcare providers, therapists, and family is crucial for maintaining independence and quality of life.
8. What are the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson disease, include:
Cognitive impairment (memory and thinking problems)
Mood disorders (depression and anxiety)
Sleep disturbances (insomnia and REM sleep behavior disorder)
Autonomic dysfunction (problems with blood pressure, bowel, and bladder control)
9. Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: Yes, several lifestyle changes can help manage Parkinson’s disease:
Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve mobility, flexibility, and balance.
Diet: A balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health.
Sleep: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and good sleep hygiene can help manage sleep disturbances.
10. How can family and friends support someone with Parkinson’s Disease?
Answer: Family and friends can provide emotional and practical support by:
Assisting with daily activities
Encouraging the patient to stay active and follow their treatment plan
Joining support groups to better understand the disease and share experiences
Providing companionship and understanding to reduce feelings of isolation and depression.
These FAQs provide a general overview of Parkinson disease,but it is important for patients and caregivers to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Some websites give more information about Parkinson’s Disease
Here are some reliable sources where you can find comprehensive and trustworthy information about Parkinson’s Disease:
Mayo Clinic: This site provides detailed information about Parkinson disease,, including symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. It also discusses complications and the impact on daily life.
Parkinson’s Disease – Mayo Clinic
Parkinson’s Foundation: Offers extensive resources on living with Parkinson’s, research updates, treatment options, and support services. They also provide genetic testing and counseling programs.
World Health Organization (WHO): Provides an overview of Parkinson disease,disease, key facts, symptoms, causes, and global health statistics. It also emphasizes the importance of accessible treatments in low and middle-income countries.
MedlinePlus: Managed by the National Library of Medicine, this site includes a wide range of information on Parkinson’s disease, from symptoms and diagnosis to treatments and living with the disease. It also links to other reputable resources.
Parkinson’s Disease – MedlinePlus
These sources provide a comprehensive understanding of Parkinson’s Disease, including current research, treatment options, and support for patients and their families.