Chickenpox: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It primarily affects children but can occur in individuals of any age. While generally a mild illness, chickenpox can lead to serious complications, especially in immunocompromised individuals, pregnant women, and newborns.
Causes
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is responsible for this disease . It spreads easily through:
Direct contact: Touching the fluid from the blisters of an infected person.
Airborne transmission: Inhaling respiratory droplets from an infected person who is coughing or sneezing.
Contaminated surfaces: Touching objects or surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Chickenpox, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, manifests through a range of symptoms that usually appear 10 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. The most common symptoms include:
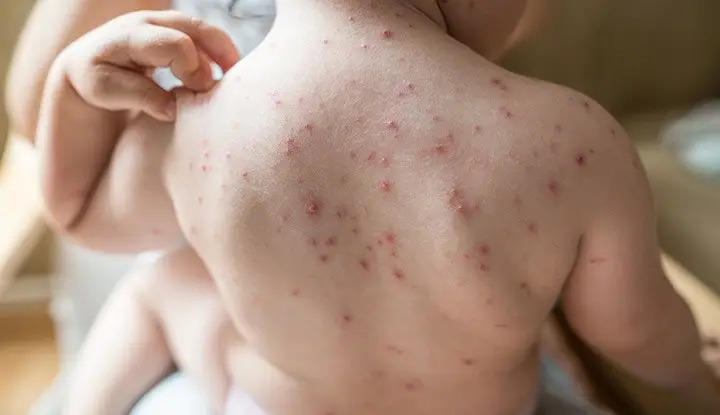
Rash:
Initial Stage: Starts as small, red spots which quickly develop into itchy, fluid-filled blisters.
Progression: These blisters eventually break and form crusts or scabs.
Distribution: The rash typically begins on the face, chest, and back, then spreads to the rest of the body, including inside the mouth, eyelids, and genital area.
Fever:
Often the first sign of chickenpox, ranging from mild to moderate.
Malaise:
General feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
Loss of Appetite:
Decreased desire to eat, often accompanying other symptoms.
Headache:
Mild to moderate headache that can occur along with the onset of fever and rash.
Fatigue:
Feeling unusually tired or weak, which can persist throughout the course of the illness.
Additional Symptoms
In some cases, individuals may experience:
Sore Throat: Mild irritation or soreness in the throat.
Muscle or Joint Pain: General aches and pains in the muscles and joints.
Complications (Rare but Serious)
While chickenpox is generally mild, it can lead to more serious complications, especially in certain high-risk groups. Symptoms indicating complications include:
Secondary Bacterial Infections: Signs include increased redness, swelling, and pain around the blisters.
Pneumonia: Symptoms like persistent cough, difficulty breathing, and chest pain.
Encephalitis: Symptoms such as severe headache, vomiting, stiff neck, and confusion or drowsiness.
Duration of Symptoms
The symptoms of chickenpox typically last about 5 to 10 days, with the blisters usually crusting over within about a week. The infectious period starts 1-2 days before the rash appears and lasts until all the blisters have formed scabs.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to seek medical advice if:
The fever lasts longer than four days or rises above 102°F (38.9°C).
The rash spreads to one or both eyes.
And the rash becomes very red, warm, or tender, indicating a possible secondary bacterial infection.
The patient experiences difficulty breathing or persistent coughing.
There are signs of severe complications, such as extreme drowsiness, confusion, or difficulty walking.
Understanding these symptoms can help in the timely identification and management of chickenpox, reducing the risk of complications and promoting a quicker recovery.
Treatment
Chickenpox usually resolves on its own without specific medical treatment, but there are several measures to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications:
Rest: Adequate rest to help the body recover.
Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Itch relief:
Baths: Take lukewarm baths with baking soda or colloidal oatmeal to relieve itching.
Topical lotions: Apply calamine lotion or other anti-itch creams.
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help reduce itching.
Fever and pain management:
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) to reduce fever and relieve pain (avoid aspirin in children due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome).
Preventing secondary infections:
Keep the skin clean and avoid scratching to prevent bacterial infections.
Trim fingernails and consider wearing gloves to minimize scratching.
Severe Cases
For individuals at higher risk of complications, such as those with weakened immune systems, antiviral medications like acyclovir (Zovirax) may be prescribed to reduce the severity and duration of the illness. It is important to start these medications as early as possible.
Prevention
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent chickenpox. The varicella vaccine is part of the routine childhood immunization schedule and is also recommended for adults who have never had chickenpox and have not been vaccinated. The vaccine is highly effective in preventing the disease or significantly reducing its severity if the infection occurs
Important Tips for Chickenpox Patients
Managing chickenpox effectively involves taking steps to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and avoid spreading the virus to others. Here are some important tips for This disease patients:
Get Plenty of Rest:
Rest is crucial for your body to fight off the infection and recover faster.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of fluids like water, herbal teas, and clear broths to stay hydrated and help your body heal.
Relieve Itching:
Baths: Take lukewarm baths with baking soda or colloidal oatmeal to soothe itchy skin.
Topical Lotions: Apply calamine lotion or other anti-itch creams to reduce itching.
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help alleviate itching but should be used as directed by a healthcare provider.
Manage Fever and Pain:
Use acetaminophen (Tylenol) to reduce fever and relieve pain. Avoid aspirin, especially in children, due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
Prevent Secondary Infections:
Keep your skin clean by gently washing with mild soap and water.
Avoid scratching the blisters to prevent bacterial infections. Keep fingernails trimmed and clean.
Consider wearing gloves, especially at night, to prevent scratching during sleep.
Wear Comfortable Clothing:
Choose loose-fitting, soft clothing to avoid irritating the blisters.
Isolate to Prevent Spread:
Stay at home and avoid contact with others, especially pregnant women, newborns, and immunocompromised individuals, until all the blisters have crusted over.
Maintain a Healthy Diet:
Eat nutritious foods to support your immune system. If you have mouth sores, opt for soft, bland foods to avoid irritation.
Monitor Symptoms:
Keep an eye on your symptoms and watch for signs of complications such as difficulty breathing, severe headache, drowsiness, or signs of a secondary bacterial infection (e.g., increased redness, warmth, or pus around the blisters).
Seek Medical Advice:
Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms worsen or if you belong to a high-risk group, such as pregnant women, infants, or individuals with weakened immune systems.
Consider antiviral medications like acyclovir if prescribed by your doctor, particularly if you are at risk for severe disease.
Practice Good Hygiene:
Wash your hands frequently with soap and water to reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
By following these tips, chickenpox patients can manage their symptoms more effectively, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure a smoother recovery. If you have any concerns or questions about your condition, do not hesitate to contact a healthcare provider for guidance.
Common Questions About Chickenpox with Answers
What is chickenpox?
Answer: This disease is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by a red, itchy rash that forms into fluid-filled blisters.
How is chickenpox spread?
Answer: Chickenpox spreads through direct contact with the blisters, respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing, and by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus.
What are the symptoms of chickenpox?
Answer: Symptoms include a red, itchy rash that turns into fluid-filled blisters, fever, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, and general malaise.
How long is a person with chickenpox contagious?
Answer: A person with chickenpox is contagious from about 1-2 days before the rash appears until all the blisters have crusted over, usually about 5-7 days after the rash starts.
Can chickenpox be prevented?
Answer: Yes, chickenpox can be prevented with the varicella vaccine, which is highly effective at preventing the disease or reducing its severity.
Can you get chickenpox more than once?
Answer: It is rare to get chickenpox more than once. However, the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate later in life as shingles (herpes zoster).
What should I do if I think I have been exposed to chickenpox?
Answer: If you have been exposed to chickenpox and are not vaccinated or have not had the disease before, contact your healthcare provider. They may recommend the varicella vaccine or antiviral medications to prevent or reduce the severity of the illness.
How is chickenpox treated?
Answer: Chickenpox treatment focuses on relieving symptoms. This includes rest, hydration, using acetaminophen for fever and pain, applying calamine lotion for itching, and taking antihistamines. In severe cases, antiviral medications like acyclovir may be prescribed.
Are there complications associated with chickenpox?
Answer: Yes, complications can include bacterial infections of the skin, pneumonia, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and in rare cases, death. Complications are more common in adults, infants, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals.
Can pregnant women get the chickenpox vaccine?
Answer: Pregnant women should not receive the chickenpox vaccine. If a pregnant woman is exposed to chickenpox, she should contact her healthcare provider immediately for advice.
What should I do if my child has chickenpox?
Answer: Keep your child at home to rest and avoid spreading the virus. Use over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and itching, ensure they stay hydrated, and keep their skin clean. Contact your healthcare provider if symptoms are severe or if your child is at high risk for complications.
How long does it take to recover from chickenpox?
Answer: Recovery from chickenpox usually takes about 1-2 weeks. The rash typically crusts over in about a week, and most people recover without lasting effects.
Is it safe for people with weakened immune systems to be around someone with chickenpox?
Answer: No, people with weakened immune systems should avoid contact with anyone who has chickenpox due to the high risk of severe complications.
What should I do if I develop a severe rash or other unusual symptoms with chickenpox?
Answer: Seek medical attention immediately if you develop a severe rash, difficulty breathing, persistent cough, high fever, severe headache, confusion, or signs of a secondary infection (e.g., increased redness, swelling, or pus).
Can chickenpox be serious in adults?
Answer: Yes, chickenpox can be more severe in adults than in children, with a higher risk of complications such as pneumonia, bacterial infections, and encephalitis. Adults should seek medical advice if they contract chickenpox.
These questions and answers provide a comprehensive overview of chickenpox, helping patients and caregivers understand the disease, its prevention, treatment, and potential complications.
Trusted websites in checkenpox
some trusted websites that provide comprehensive information about this disease :
Cleveland Clinic:
Offers detailed information on causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention, and complications of chickenpox.
Chickenpox: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
NHS (National Health Service, UK):
Provides an overview of chickenpox, including symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Mayo Clinic:
Explains the causes, risk factors, complications, and prevention of this disease .
Chickenpox – Symptoms and causes
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
Detailed information on symptoms, complications, vaccination, and management of chickenpox.
Chickenpox Symptoms and Complications | CDC
These sources provide reliable and comprehensive information on chickenpox, including its symptoms, treatment options, prevention, and potential complications.
Conclusion
Chickenpox, while often mild in healthy children, can pose significant risks to certain populations. Prevention through vaccination is key, and managing symptoms effectively can help ensure a smooth recovery. If complications arise or if you belong to a high-risk group, seek medical advice promptly.